What Is Cognitive Dissonance? A Definition For Educating
Understanding Cognitive Dissonance: A Psychological Framework for Development and Studying
Human beings attempt for consistency between their ideas, beliefs, and actions.
When an inconsistency arises—when beliefs and behaviors conflict—it creates a way of discomfort or rigidity often known as cognitive dissonance.
This idea, first launched by psychologist Leon Festinger in 1957, supplies perception into how people reply to battle inside themselves and the way they work to resolve inside contradictions. Its implications stretch throughout fields like psychology, decision-making, conduct modification, and, crucially, schooling.
What Is Cognitive Dissonance?
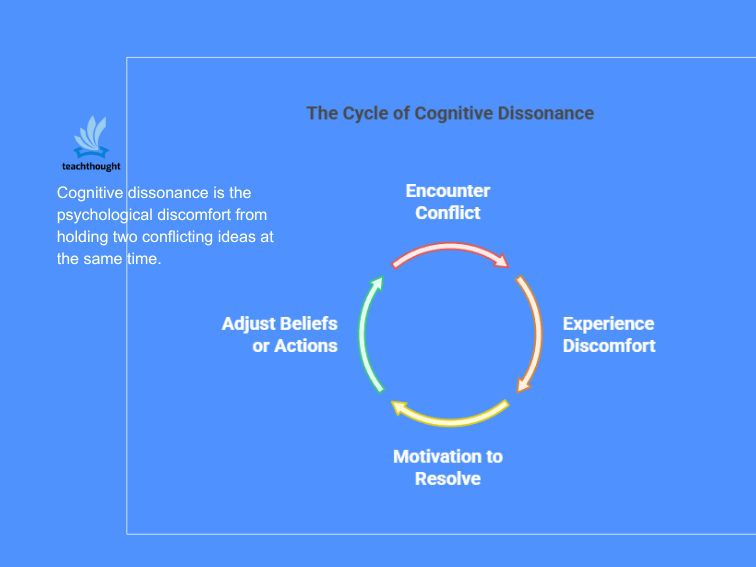
Cognitive dissonance is the psychological discomfort that arises when a person encounters a battle between what they imagine and the way they behave, or between two competing beliefs. This psychological rigidity arises as a result of human beings are wired to hunt alignment between their cognition (beliefs, attitudes, data) and their conduct. When dissonance happens, it acts as a motivator to handle and resolve the inconsistency.
For instance, a scholar who values educational achievement however fails to review for an upcoming check experiences dissonance. Their perception, “Finding out is necessary for fulfillment,” conflicts with their conduct of procrastination. This rigidity prompts them to take motion—both by altering their conduct (learning) or by rationalizing it (“This check isn’t that necessary”).
How Does Cognitive Dissonance Work?
Cognitive dissonance operates as a psychological self-regulation instrument, pushing people to revive concord between conflicting ideas or behaviors. Folks sometimes reply to cognitive dissonance in one in every of 3 ways:
- Altering Beliefs: Adjusting one’s view to make it suitable with their conduct.
Instance: As a substitute of believing that onerous work results in success, a scholar may conclude that exterior components, like luck, matter extra. - Altering Behaviors: Aligning one’s actions with pre-existing beliefs.
Instance: A scholar who procrastinates on learning decides to put aside time to arrange after acknowledging the significance of educational effort. - Rationalizing the Battle: Including new justifications to resolve the strain with out altering beliefs or behaviors.
Instance: A instructor justifies slicing corners on lesson prep by telling themselves, “I’m more practical once I train on the fly.”
The mind’s purpose is to cut back the dissonance as effectively as doable, and the tactic chosen typically depends upon which possibility is best or least threatening to 1’s sense of identification.
Cognitive Dissonance in Training
In educating and studying environments, cognitive dissonance typically happens when college students or educators encounter new data or experiences that problem their present beliefs or practices. Whereas this discomfort may really feel unproductive at first, it’s really a strong instrument for progress.
Listed below are three key methods cognitive dissonance manifests in schooling:
1. Selling Essential Considering
College students who’re confronted with new concepts or proof that contradict their present understanding typically expertise cognitive dissonance. For instance, a center college science scholar studying about local weather change may wrestle to reconcile their household’s routine use of disposable plastics with the brand new data that plastic air pollution harms ecosystems. This rigidity forces the scholar to both reject or combine the brand new data, encouraging deeper inquiry into the subject.
Academics can deliberately create these “productive discomfort” moments by presenting open-ended questions, difficult assumptions, or introducing dilemmas related to college students’ lives. When college students replicate on how their beliefs align—or don’t align—with the proof, they interact in vital considering and develop extra complicated, nuanced views.
2. Encouraging Behavioral Change
Cognitive dissonance highlights the hole between beliefs and actions, motivating college students to adapt their conduct to align with their values. As an example, excessive schoolers who really feel enthusiastic about environmental sustainability however usually litter may change their habits after studying a persuasive essay on the implications of air pollution. Equally, a scholar who believes within the significance of punctuality however repeatedly misses deadlines might start utilizing group instruments to keep away from these inconsistencies.
Educators can leverage this phenomenon by way of interventions and purpose setting. When college students acknowledge how their present conduct undermines their targets, they’re extra prone to take actions to create concord.
3. Enhancing Educator Practices
Cognitive dissonance isn’t restricted to college students; educators expertise it as properly. A instructor may imagine within the worth of differentiated instruction however really feel overwhelmed by time constraints, reverting to a one-size-fits-all strategy. This conflict between perception and observe can immediate reflection, main the instructor to hunt small, manageable methods to include differentiation into their routines.
Skilled growth typically leverages cognitive dissonance by introducing methods or proof that push lecturers to look at and query their present approaches. For instance, studying in regards to the optimistic affect of student-centered studying may inspire lecturers to regulate their tutorial practices.
Overcoming Cognitive Dissonance within the Classroom
Whereas cognitive dissonance could be a highly effective driver of change, it may possibly additionally result in resistance or defensiveness if left unmanaged. Listed below are some methods educators can use to assist college students and colleagues productively navigate dissonance:
- Normalize Discomfort: Reassure college students and friends that it’s okay to really feel uncomfortable when encountering new concepts. Body cognitive dissonance as a pure, even wholesome, a part of studying and progress.
- Foster Reflection: Encourage college students to ask questions like, “Why do I really feel conflicted?” or “How can I align my actions with my beliefs?” Journals, discussions, or self-assessments can create house for this reflection.
- Assist Change Regularly: As a substitute of anticipating fast transformation, present alternatives for small, manageable steps towards resolving inconsistency.
- Present Proof and Counterexamples: The extra data college students and colleagues have entry to, the higher geared up they’re to judge their assumptions and act thoughtfully.
Conclusion
Cognitive dissonance is a psychological phenomenon that happens when beliefs, values, or actions contradict each other, creating a way of psychological discomfort. Whereas this rigidity may be unsettling, it is usually a vital driver of reflection, change, and important considering. For educators, understanding cognitive dissonance affords a possibility to create a studying atmosphere the place college students really feel challenged however supported as they confront inconsistencies of their ideas and behaviors.
By leveraging the facility of cognitive dissonance, educators can deepen scholar studying, encourage progress, and foster mental curiosity, making certain that each college students and lecturers frequently attempt for self-improvement of their pursuit of data and understanding.
What Is Cognitive Dissonance? A Definition For Educating

